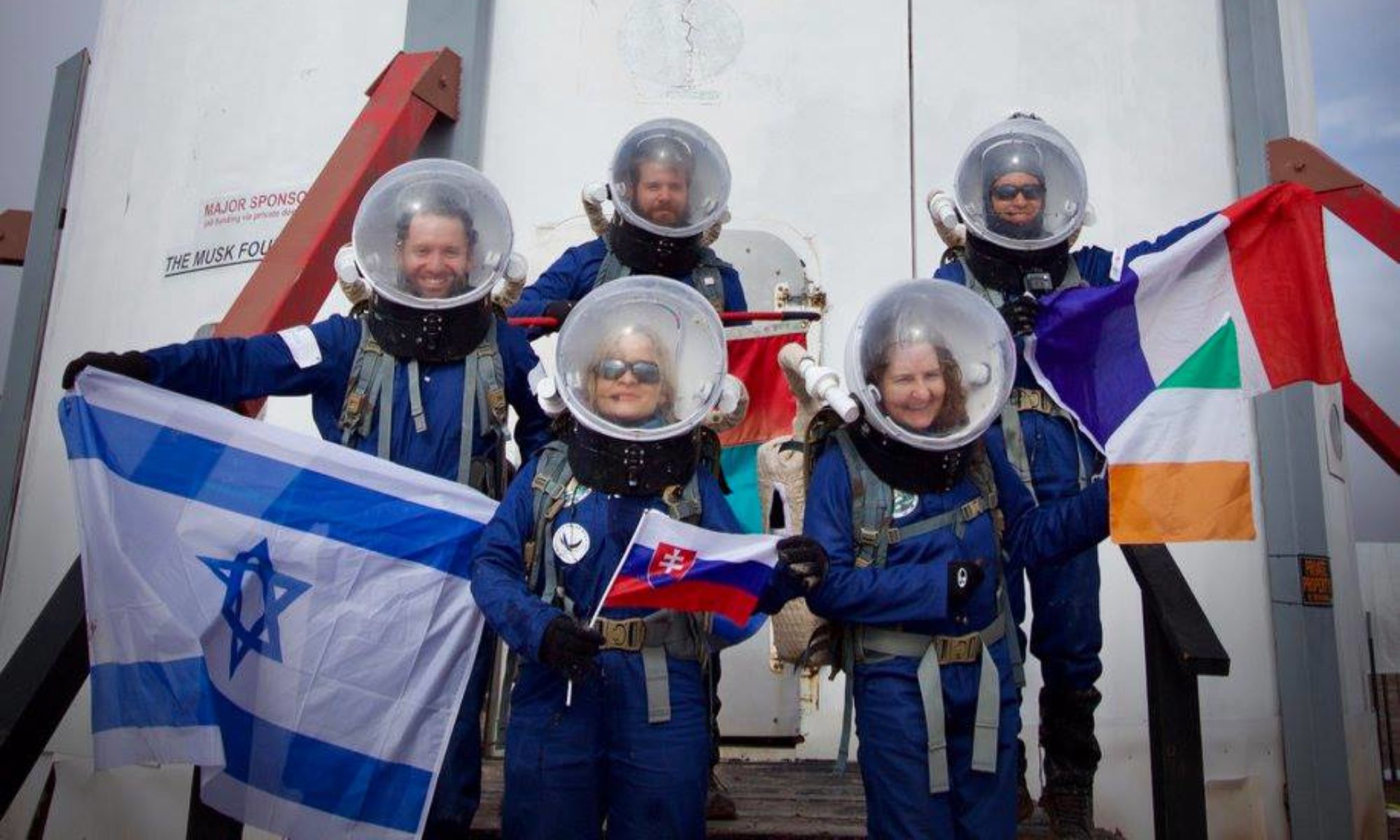
Mission Name: MARS EXPRESS (MDRS Advanced Research Study, EXperimental Pressure suit Radios Engineering Story Simulation)
For MDRS, this was an unusual rotation. We were on a one week mission rather than two weeks, and five crew members rather than six. We drove in from five different states in three time zones, with goals to improve engineering at MDRS in areas we’ve been working on for years in the background.
Pressurized Spacesuits and YouTube Livestream
Our mission sponsor, Peter, wanted to test his pressurized space suit designs within the hab. He also had extensive plans to film this with professional equipment with a short “drama” depicting Cody in the pressurized suit going through the airlock and ascending the stairs to pretend to patch the main window. This succeeded in most respects with him easily getting up the staircase (our biggest worry). The suit itself had several minor breakdowns during assembly and during the filming, but all were remedied on site. We are very pleased with the results.
Cody, a YouTube geologist with 2.2 million followers, did a livestream of Peter helping him into the spacesuit and as a “behind the scenes” live stream of the drama video in real time. As of now (two days later), this video has 33,000 views and 1000 likes. Kent worked the camera/comments for the suiting up part and then put on a conventional analog suit to appear as the backup astronaut during the video, and Brad took over the live stream. A friend of the Mars Society in the comments answered questions for late arrivals wondering what Cody was doing, and the behind the cell phone camera team also answered questions when possible. Overall a very good experience, showing both the successes and setback/recovery process for spacesuit engineering and film production in a single hour and a half video.
Peter also did several Discord live streams following us around with a laptop and doing interviews while we went about our work. He set up an elaborate HAM radio setup in the RAM maintenance building and was able to communicate with one other HAM operator in Arizona over the mission during the window when it was operational.
Crew EVA Link Expansion
Brad and Peter are the software and hardware leads, respectively, on Crew EVA Link, and Kent is the creator of the concept. We spent three years developing this system to track the safety and data of MDRS crews, and it went live as an operational system last year. By having all three of us at the hab to test it as analog astronauts, we gained a lot of insight into the pain points and successes of the system in unexpected ways. Brad discovered how difficult it was with the base system to send and receive messages from the field in the current form. We set up a new relay tracker on a hilltop to cover areas north and slightly east of the hab and were able to troubleshoot issues with it in days that would have taken weeks remotely. We now have what we need to roadmap the next year of development to further improve the system.
Brad also extended the system with a system that can link the voice communications to Discord when requested. Experiments linking HAM and other advanced systems produced mixed results, but were promising.
RC Rover Testing
Kent won a NASA design competition last year to design a rover for the steep craters at the Lunar South Pole. While that design used six methods to keep the rovers from tumbling into the dark abyss, three of those methods were possible to test using 1:10 scale toy remote control tanks modified to link together, have outrigger stabilizers, and record data using cell phone gyroscope logging software. Over three tests, the rovers were reconfigured in different ways to expand the data set. All rovers survived and the data is better than expected. The core principles of using them in a “land train” to compensate for slippage on one unit and instantly tow or push it back to steady ground were validated, as were the outriggers to avoid flips. That said, the conditions were so dry that the top 5 cm of soil was instantly crumbling and avalanching down the hillside when disturbed by the tank treads, which was a problem since the ground clearance on 1:10 scale rovers was less than 2 cm. So they rarely reached the 25-degree success criteria planned because they were simply too small. The experiment is considered a success because the rovers survived desert conditions, the data was logged, and the limits of nature and scale were added to the solution space in a more realistic way than originally envisioned. The R/C rovers will be tested in tamer conditions this Spring with an inclined wall panel to get “lab” baseline data and compared with the field data. A follow-up study with larger rovers can be designed. Ironically, the size and weight limits of the University Rover Challenge would be ideal for such a test at MDRS, if the teams want to make “land trains” of rovers of compatible heights and log their results after a URC competition, I’m certainly willing to help design that follow-on experiment.
Balloon Experiments
Kent has a business model involving clear plastic radiation recorders – sort of like a permanent cloud chamber, for recording cosmic ray doses en route to and from Mars. When originally envisioned seven years ago this was purely theoretical, but through his work with the Inspired 24 Innovation team he found several scientists working on a thin plastic film that can record radiation if “developed” (like photographic film) with an lye solution. While not ideal, it’s close enough for further work. While 100 percent purity is ideal, the samples were not secured in time so 75 percent off the shelf panels were brought to MDRS. The idea was to launch them on a fast weather balloon to receive primary cosmic rays briefly and then return. Since the crew were driving in five different directions after departure, this permitted whoever was closest to be the “chase crew” for the payload. This would also use Meshtastic (the system used for Crew EVA Link) as a balloon tracker. Weather never cooperated long enough for this launch, so the materials and plan will be transferred from Kent to Cody to try to find an opportunity shot off his remote ranch, and possibly make it a YouTube show topic. If the experiment works with off the shelf 75 percent materials, this has dramatic benefits for STEM education since any school or club could effectively “sample” exploding stars directly via weather balloons rather than simply launch toys and cameras.
While that experiment was on hold, an accidental experiment caused much excitement. Peter had a smaller balloon holding an unprotected SenseCap Meshtastic device to use as a relay for our long-range EVA test. The line anchoring this balloon 30 meters up snapped and sent the credit-card sized radio tracker with GPS on a journey we could track on our Crew EVA Link display. Our last signal was from north of Parachute, Colorado. It was 166 miles away, with the tracker moving at 217 miles per hour at 34,616 feet of altitude. Since it was unprotected (never intended to be more than a few feet above the ground), the uninsulated battery probably froze out at 86 percent battery life, or we simply lost it over the horizon from our most distant tracker. Since it was on Meshtastic, which is a global relay network, there were stations in close proximity that could have bounced the signal further back to us had it continued another 50 miles. It’s also possible the balloon simply popped and that speed was the descent into a mountain north of town. Ironically, Kent stayed in Parachute on the road trip to MDRS and had a picture of that mountain from a few days earlier.
Soil Sampling
Kent and Cody each had separate soil sample experiments that were performed in concert on a single EVA just as a rainstorm hit. Kent wanted test tube samples of each color change in the layers of soil near the hab, with GPS coordinates of each sample site, for later analysis. Cody wanted a dry soil sample to desiccate out for his science education videos. Both managed to “speed run” this collection and even get some good photos as the rain moved in. Matthias was also indispensable as a second set of hands to make the sample collections literally ten times faster than otherwise possible.
Advanced Photo Surveys
Peter brought in advanced 360 cameras with 60-megapixel sensors and photographed the outpost structures in detail. Such photo surveys are great for identifying maintenance issues early and documenting the state of the facility. Kent and Brad also did Quest 3 Hyperscape surveys of the hab upstairs, greenhab, and science dome to give a photorealistic VR experience.
Repairs and Upgrades
Matthias and Anderson spent several hours working on the toilet holding tank Friday to prepare it for the next two missions prior to the next work party. This operation was successful, and some upgrades are planned for that party to avoid future problems.
Peter tested several Toughbook laptops that contain hardware that can connect to Crew EVA Link while being operated in EVA. This will enable crews to collect field data while in the field. We also tested a mount for the side-by-side rovers that would be installed in the passenger side. We have enough data now to design and build permanent solutions that can be donated later to MDRS. We also tested a permanent mount so that each rover can be tracked and function as a relay on the Crew EVA Link network.
Other Notes – Fossils of Past Civilization
On the hike to set up the repeater north of the hab, we discovered a boom box, typewriter in the case, and VCR shoved under boulders deep in the desert. Matthias decided to restore the typewriter as a project. After our middle-aged crew found all these artifacts from the 1990’s, we have met the dinosaurs, and they are us. 🙂
Overall this was a very successful if brief mission and we are very happy with the results.
Kent Nebergall, Commander, MDRS Crew 329













You must be logged in to post a comment.